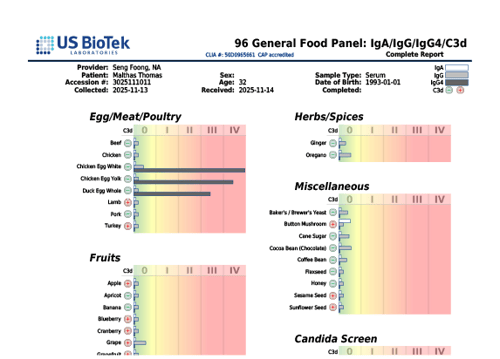
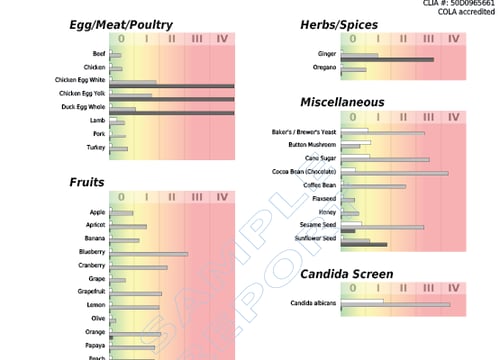
GI - Basic Profile
The GI–Basic Profile is US BioTek’s entry-level GI Microbiome Profile measuring 104 markers from 8 GI testing categories. The profile uses state-of-the-art technology to offer results based on cellular DNA, providing sensitive, accurate, and reproducible results.
- GENERAL MACROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION
-
KEY PHYLA % COMMENSAL ABUNDANCE
-
PARASITES & WORMS
-
OPPORTUNISTIC BACTERIA
-
POT. AUTOIMMUNE TRIGGERS
-
FUNGI & YEAST
-
BACTERIAL PATHOGENS
-
VIRAL PATHOGENS
-
NORMAL BACTERIA/FLORA

PCR
RT-PCR at US BioTek offers precise detection of pathogen nucleic acids, capitalizing on FDA-authorized technology for accurate DNA/RNA analysis.
ELISA
ELISA utilizes advanced automation for reliable blood analysis, detecting specific antibodies or antigens via spectrophotometry.
Macroscopy
Stool macroscopy involves a thorough visual examination to identify abnormalities such as blood and parasites in samples.
Culture
Our stool culture method incubates specimens to grow and identify bacteria through colony appearance and biochemical testing.
This test can be run on Stool samples.
| Specimen Requirement | |
| Stool Transport Tubes | 2 |

4 Simple Steps to Results
Steps 1
ORDER THE KIT
Collection Kits are free for US BioTek account holders and ship within 1 business day
Steps 2
COLLECT SAMPLE
Kits are designed for the simplest & most hygienic collection process possible
Steps 3
SHIP SAMPLE
Prepaid return shipping labels are included making shipping simple

Steps 4
RECIEVE RESULTS
Results are delivered to the provider portal with industry leading turnaround times.
General Macroscopic Description
- Stool Color
- Stool Form
- Mucous
- Occult Blood
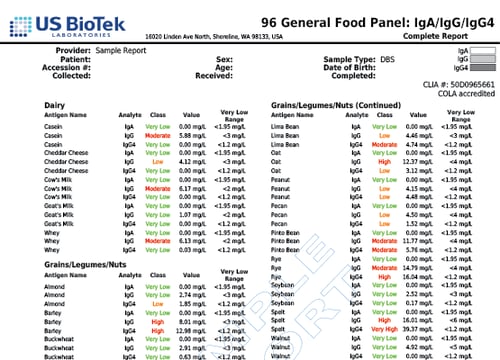
Key Phyla % Commensal Abundance
- Bacteroidetes
- Firmicutes
- Firm/Bact Ratio
- Proteobacteria
- Actinobacteria
- Verrucomicrobia
- Euryarchaeota
Parasites & Worms
- Cryptosporidium
- Ent. Histolytica
- Enterocytozoon species
- Cyclospora cayetanensis
- Giardia Intestinalis
- Blast. hominis
- Dient. Fragilis
- Ascaris lumbricoides, round
- Necator americanus,hook
- Trichuris trichuria, round
- Taenia species, tape
- Enterob. Vermicularis
- Strongyloides stercoralis
- Enterocytozoon spp
- Hymenolepis spp
Opportunistic Bacteria
- Bacillus sp.
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Enterococcus faecium
- Morganella sp.
- Pseudomonas sp.
- Pseud. aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus sp.
- Staph. aureus
- Streptococcus species
- Streptococcus aureus
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Streptococcus anginosus
- Streptococcus mutans
- Streptococcus oralis
- Streptococcus salivarius
- Methanobacteriaceae
- Desulfovibrio piger
- Enterobacter sp.
- Phocaeicola vulgatus
- Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
Pot. AutoImmune Triggers
- Citrobacter sp.
- Citrobacter freundii
- Klebsiella sp.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Prevotella copri
- Proteus sp.
- Proteus mirabilis
- Fusobacterium sp.
Fungi & Yeast
- Candida sp.
- Candida albicans
- Candida dubliniensis
- Candida glabrata
- Candida intermedia
- Candida krusei
- Candida lambica
- Candida lusitaniae
- Candida parapsilosis
- Candida famata
- Candida kefyr
- Candida lipolytica
- Geotrichum sp.
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Rhodotorula sp.
Bacterial Pathogens
- Aeromonas sp.
- Campylobacter sp.
- difficile, Toxin A
- difficile, Toxin B
- Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli
- Enteroinvasive E. coli/Shigella
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli LT/ST
- Shiga-like toxin E. coli stx 1
- Shiga-like toxin E. coli stx 2
- Enteroaggregative E. coli
- Enteropathogenic E. coli
- E. coli O157
- Hypervirulent Clostridium difficile
- Salmonella sp.
- Vibrio spp
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Helicobacter pylori PCR & EIA
- H. pylori virulence factors (x11)
- H.Pylori antigen
Viral Pathogens
- Adenovirus 40/41
- Norovirus GI/II
- Rotavirus
- Sapovirus (I,II,IV,V)
- Astrovirus (hAstro)
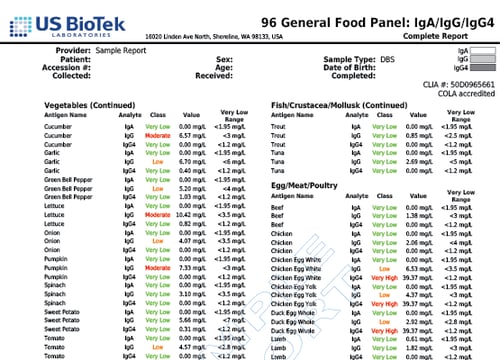
Normal Bacteria/Flora
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Bifidobacterium sp.
- Bifidobacterium longum
- Bifidobacterium adolescentis
- Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Bifidobacterium breve
- Oxalobacter formigenes
- Lactobacillus species
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Lactobacillus casei
- Lactobacillus delbrueckii
- Lactobacillus plantarum
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Lactobacillus salivarius
- Clostridium sp.
- Oxalobacter formigenes
- Akkermansia muciniphila
- Faecalibacterium prausnitzii
Markers Tested
General Macroscopic Description
- Stool Color
- Stool Form
- Mucous
- Occult Blood
Key Phyla % Commensal Abundance
- Bacteroidetes
- Firmicutes
- Firm/Bact Ratio
- Proteobacteria
- Actinobacteria
- Verrucomicrobia
- Euryarchaeota
Parasites & Worms
- Cryptosporidium
- Ent. Histolytica
- Enterocytozoon species
- Cyclospora cayetanensis
- Giardia Intestinalis
- Blast. hominis
- Dient. Fragilis
- Ascaris lumbricoides, round
- Necator americanus,hook
- Trichuris trichuria, round
- Taenia species, tape
- Enterob. Vermicularis
- Strongyloides stercoralis
- Enterocytozoon spp
- Hymenolepis spp
Opportunistic Bacteria
- Bacillus sp.
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Enterococcus faecium
- Morganella sp.
- Pseudomonas sp.
- Pseud. aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus sp.
- Staph. aureus
- Streptococcus species
- Streptococcus aureus
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Streptococcus anginosus
- Streptococcus mutans
- Streptococcus oralis
- Streptococcus salivarius
- Methanobacteriaceae
- Desulfovibrio piger
- Enterobacter sp.
- Phocaeicola vulgatus
- Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
Pot. AutoImmune Triggers
- Citrobacter sp.
- Citrobacter freundii
- Klebsiella sp.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Prevotella copri
- Proteus sp.
- Proteus mirabilis
- Fusobacterium sp.
Fungi & Yeast
- Candida sp.
- Candida albicans
- Candida dubliniensis
- Candida glabrata
- Candida intermedia
- Candida krusei
- Candida lambica
- Candida lusitaniae
- Candida parapsilosis
- Candida famata
- Candida kefyr
- Candida lipolytica
- Geotrichum sp.
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Rhodotorula sp.
Bacterial Pathogens
- Aeromonas sp.
- Campylobacter sp.
- difficile, Toxin A
- difficile, Toxin B
- Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli
- Enteroinvasive E. coli/Shigella
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli LT/ST
- Shiga-like toxin E. coli stx 1
- Shiga-like toxin E. coli stx 2
- Enteroaggregative E. coli
- Enteropathogenic E. coli
- E. coli O157
- Hypervirulent Clostridium difficile
- Salmonella sp.
- Vibrio spp
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Helicobacter pylori PCR & EIA
- H. pylori virulence factors (x11)
- H.Pylori antigen
Viral Pathogens
- Adenovirus 40/41
- Norovirus GI/II
- Rotavirus
- Sapovirus (I,II,IV,V)
- Astrovirus (hAstro)
Normal Bacteria/Flora
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Bifidobacterium sp.
- Bifidobacterium longum
- Bifidobacterium adolescentis
- Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Bifidobacterium breve
- Oxalobacter formigenes
- Lactobacillus species
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Lactobacillus casei
- Lactobacillus delbrueckii
- Lactobacillus plantarum
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- Lactobacillus salivarius
- Clostridium sp.
- Oxalobacter formigenes
- Akkermansia muciniphila
- Faecalibacterium prausnitzii
VeriTek Process

AUTOMATED SYSTEMS

SUPERIOR ASSAY PREPARATION

DUPLICATE TESTING

EXTERNAL ACCOUNTABILITY
Need Assistance With
Specimen Collection?
Accurate results start with proper specimen collections. Watch the video or download detailed instructions to walk you through the collection process.